Introduction
In today’s fast-paced business world, efficiency is more important than ever. Companies are constantly seeking ways to reduce manual work, streamline operations, and improve productivity. One solution that has gained significant attention is Business Process Automation (BPA). Business process automation allows organizations to use technology to perform repetitive tasks without human intervention, freeing employees to focus on more strategic activities.
Businesses of all sizes—from startups to large enterprises—can benefit from automating processes. Whether it is managing invoices, processing customer requests, or tracking inventory, automation ensures accuracy, speed, and consistency. Furthermore, it can reduce operational costs, minimize errors, and improve customer satisfaction.
However, understanding what business process automation is, why it matters, and how to implement it correctly is crucial for success. Without proper planning, automation efforts can fail or even create new problems. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the concept of business process automation, its importance, step-by-step implementation, benefits, risks, common mistakes, expert tips, and frequently asked questions. By the end of this guide, you will have a solid understanding of how Business process automation can transform your organization.
Whether you are a business owner, manager, or someone new to process automation, this guide is designed to make the topic simple and actionable. Let’s dive in and explore how automation can revolutionize the way your business operates.
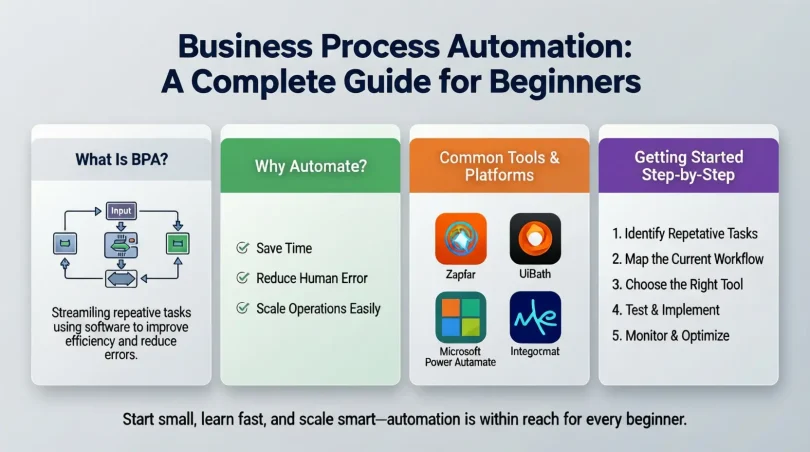
What is Business Process Automation?
Business Process Automation (BPA) is the use of technology to automate recurring business tasks or workflows. It involves replacing manual, repetitive tasks with automated solutions to improve efficiency, reduce errors, and save time. BPA is more than just using software; it’s about analyzing processes, identifying inefficiencies, and applying technology strategically to streamline operations.
For example, a company may use automation to:
- Automatically send email responses to customer inquiries
- Process payroll without manual entry
- Track inventory and reorder products when stock is low
- Generate reports from various departments without human effort
Automation can involve a variety of tools, including workflow automation software, robotic process automation (RPA), and AI-driven systems. The key idea is to reduce human effort on repetitive tasks while ensuring tasks are completed accurately and consistently.
BPA is different from simple task automation because it focuses on end-to-end processes. Instead of automating one small task, it looks at entire workflows and optimizes them from start to finish. This holistic approach can save businesses a significant amount of time, resources, and money.
Why is Business Process Automation Important?
Implementing Business process automation is no longer a luxury; it has become essential for businesses that want to remain competitive. Here are the key reasons why BPA is important:
- Efficiency Improvement
Automated processes run faster than manual ones. By eliminating repetitive tasks, employees can focus on value-added activities that require creativity and critical thinking. - Cost Reduction
Automation reduces labor costs and minimizes human errors that can lead to expensive mistakes. - Consistency and Accuracy
Machines follow predefined rules and workflows consistently. This ensures that tasks are performed accurately every time. - Enhanced Customer Experience
Automated processes such as instant email responses, order tracking, and chatbots improve customer satisfaction by providing faster and reliable service. - Scalability
Businesses can scale operations without proportionally increasing staff. Automation allows handling more transactions, clients, or tasks without additional resources. - Data Management and Reporting
BPA systems can collect and analyze data automatically, providing insights for better decision-making. - Compliance and Risk Management
Automated workflows reduce the risk of non-compliance with regulations by maintaining accurate records and following standardized procedures.
In short, businesses that adopt BPA can work smarter, not harder. It’s about leveraging technology to optimize performance while keeping costs under control.
business process automation a complete guide for beginners

Implementing Business process automation requires a structured approach. Below is a detailed guide to help you automate your business processes successfully.
Step 1: Identify Processes to Automate
Not all business processes are suitable for automation. Start by analyzing your operations and identifying tasks that are:
- Repetitive and rule-based
- Time-consuming
- Prone to errors
- High-volume
Common examples include invoice processing, customer support ticketing, payroll, and inventory management.
Step 2: Map Your Current Workflow
Before automation, it is essential to understand the existing workflow. Document every step of the process, including approvals, decision points, and data inputs. This step helps identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks that can be eliminated.
Step 3: Choose the Right Automation Tools
Select tools that fit your business needs. Some popular automation solutions include:
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Ideal for repetitive data entry and rule-based tasks
- Workflow Automation Software: Helps manage multi-step processes across teams
- AI-Powered Tools: Useful for predictive tasks, customer support, and decision-making
- ERP Integration: Automates core business processes such as finance, HR, and supply chain
Step 4: Define Automation Goals
Set clear objectives for your automation project. Goals may include reducing processing time, minimizing errors, or improving customer response times. Having measurable goals ensures that your automation efforts are effective.
Step 5: Design the Automated Workflow
Use your process map to design an automated workflow. Define triggers, actions, rules, and approvals. Make sure the design is logical and covers all possible scenarios.
Step 6: Test the Automation
Before going live, thoroughly test the automated workflow. Check for errors, inefficiencies, and unexpected outcomes. Testing ensures that automation delivers the desired results without disrupting operations.
Step 7: Implement Automation
Once testing is complete, deploy the automation system. Ensure that employees are trained on using the new tools and understand how the automated process works.
Step 8: Monitor and Optimize
Automation is not a one-time task. Monitor performance regularly and collect feedback. Use data analytics to identify areas for improvement and optimize workflows over time.
Step 9: Scale Automation
After successful implementation in one area, consider scaling automation to other processes. Start with high-impact tasks that can further improve efficiency and cost savings.
Benefits of Business Process Automation
Implementing business process automation offers multiple benefits for businesses. Here are the key advantages:
- Time Savings: Automation reduces manual effort and speeds up repetitive tasks.
- Cost Reduction: Less manual work and fewer errors result in significant cost savings.
- Improved Accuracy: Automated processes are consistent and error-free.
- Better Productivity: Employees can focus on strategic and creative tasks.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Faster and more accurate service improves the customer experience.
- Data Insights: Automation generates data that can be analyzed for better decision-making.
- Compliance: Standardized processes help meet regulatory requirements consistently.
- Scalability: Automation allows businesses to handle increased workloads without hiring more staff.
For example, a company using BPA for invoice processing can reduce the time taken from days to hours, while also eliminating errors in calculations or approvals.
Disadvantages / Risks of Business Process Automation
While BPA has numerous advantages, it is not without risks. Businesses should be aware of potential disadvantages:
- High Initial Cost: Implementing automation tools can be expensive initially.
- Complexity: Designing and integrating automation systems can be complicated.
- Employee Resistance: Staff may resist changes due to fear of job loss.
- Dependency on Technology: Over-reliance on automated systems can create problems if tools fail.
- Maintenance Requirements: Automation systems require regular updates and monitoring.
- Limited Flexibility: Automation works best for predictable tasks, not creative or unpredictable work.
Understanding these risks helps businesses plan better and implement BPA successfully without major setbacks.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Many businesses fail in their automation journey due to avoidable mistakes. Here are some common pitfalls:
- Automating Inefficient Processes
Automating a flawed process only makes inefficiency faster. Optimize the workflow first before automating. - Ignoring Employee Training
Without proper training, employees may struggle to adapt to automation tools. - Overlooking Testing
Skipping testing can result in errors and process disruptions after deployment. - Lack of Clear Goals
Without measurable objectives, it’s hard to gauge the success of automation. - Neglecting Data Security
Automation often involves sensitive data. Failing to secure it can lead to breaches. - Over-Automation
Not every task should be automated. Some tasks require human judgment and creativity.
Avoiding these mistakes increases the likelihood of a smooth and successful automation implementation.
FAQs About Business Process Automation
1. What types of processes can be automated?
Processes that are repetitive, rule-based, and high-volume are ideal for automation. Examples include data entry, payroll processing, customer support ticketing, and order management.
2. How much does business process automation cost?
Costs vary depending on the complexity, tools used, and scale of automation. Initial investment can be high, but long-term savings often outweigh the costs.
3. Will automation replace human jobs?
Automation replaces repetitive tasks, not creative or strategic work. Employees can focus on more valuable tasks while automation handles mundane work.
4. How long does it take to implement BPA?
Implementation time depends on the complexity of the process and the tools used. Simple tasks can be automated within days, while large workflows may take weeks or months.
5. Can small businesses benefit from automation?
Absolutely. Even small businesses can automate accounting, email marketing, inventory tracking, and customer service to save time and improve efficiency.
6. How do I choose the right automation tool?
Consider factors like ease of use, integration capabilities, scalability, cost, and support. Tools should align with your business goals and workflow requirements.
7. Is BPA the same as robotic process automation (RPA)?
RPA is a type of BPA that uses software robots to perform specific tasks. BPA is a broader concept that includes end-to-end workflow automation.
8. How can I measure the success of automation?
Measure key performance indicators (KPIs) such as time saved, cost reduction, error rate, customer satisfaction, and employee productivity.
Expert Tips & Bonus Points
- Start Small: Begin with a single process to minimize risk and gain experience.
- Involve Employees: Include staff in planning to reduce resistance and get valuable insights.
- Use Analytics: Leverage data to track performance and identify improvement areas.
- Regular Updates: Keep automation tools updated to maintain efficiency and security.
- Balance Automation and Human Effort: Automate repetitive tasks but retain human oversight for critical decisions.
- Document Processes: Maintain clear documentation of automated workflows for training and troubleshooting.
- Consider Cloud Solutions: Cloud-based automation tools offer scalability and flexibility.
Bonus Tip: Integrate BPA with AI technologies like machine learning and predictive analytics to unlock advanced automation capabilities, such as anticipating customer needs or detecting process anomalies before they occur.
Conclusion
Business Process Automation is transforming the way companies operate. By automating repetitive and rule-based tasks, organizations can increase efficiency, reduce errors, save costs, and enhance the overall customer experience. Whether it is processing invoices, managing customer service, or tracking inventory, automation allows employees to focus on strategic and creative work.
However, successful automation requires careful planning, the right tools, clear goals, and employee involvement. Avoiding common mistakes and continuously monitoring workflows ensures that automation delivers its full benefits. While there are risks and initial costs, the long-term advantages of business process automation far outweigh these challenges.
For businesses looking to remain competitive and agile, embracing Business process automation is no longer optional—it is a necessity. By starting with small, manageable processes and gradually scaling, any organization can leverage the power of automation to drive growth, improve productivity, and enhance customer satisfaction. With thoughtful implementation and continuous improvement, BPA can revolutionize the way your business operates.